Define Methods Strings
In java
String is an object, which represent the sequence of characters or collection
of characters. In java string class is used to create Sting object. There are
two ways to create String object in java
o
By literal method
o
By new keyword
String Object - Creating String object Methods
Literal
Method for creating String object
Literal String
is look like same as primitive data type, when we create any String literal
then that String reserved a special memory area known as string contact pool.
String Object - creating String object Methods
Syntax:
String name = “string value”;
New
keyword method for creating String object
New keyword
String is a non-primitive data type
Syntax:
String name = new String (“some
value”); // constructor
When we
declare any object with keyword than it means we are creating constructor (we
will have learnt about constructor later). So string is a class and we create
its constructor. When we create String constructor then JVM create two object
with one reference. As for non-primitive type it will reserve are for memory in
HEAP and also at string constant pool.
String Object - creating String object Methods
Example:
In java
there are two concepts came with String which are following:
o Immutable
o
Mutable
Immutable
String
Immutable string
are those Strings which are not changed, whenever we create a string and we
want to modify its value, but we can’t modify it original value. JVM create new
object instead of change its value.
String Object - creating String object Methods
Example:
Now let understand
the above example in details. First I create String literal with reference name
and assign value “Smart”, when I combine name reference with other
string then JVM create another instance with same reference in string
constant pool. But reference variable refers the original value. So, if you
want to access the other instance then explicitly assign it.
String Object - creating String object Methods
Note:
here I implicitly change the instance of reference, but still Smart
value exist.
Mutable
String
The string
whose value is changed is known as Mutable String. For creating mutable
String Java provides the StringBuffer and StringBuilder Classes
StringBuffer
class Example
StringBuilder class
example:
Now question
is raised that if String buffer and Builder doing same thing than
why we need two different classes? If there is any different between both of
them? Answer is yes, there is some difference
1. String Buffer class
is a synchronized class, in this class it is thread is safe and String
buffer is less efficient then String Builder. On other hand the String
Builder class is a non-synchronized class, in this class thread is not safe
and String builder is more efficient then String Buffer.
String Object - creating String object Methods
String Methods
Following
are the String Methods
String Object - Creating String object Methods
Java
String charAt
o
This method return
character at specified index.
o
It index start from zero
o Example:
1.
Java String
Compare To
o
This method compares two
string by its value and return integer value. If values are same return 0, if
first string is greater than second string then return positive number
and first string is less than the second string it return negative number.
Example:
Java
String concat
o
This method combines the
specified string with current string variable.
o Example
Java
String contains
o
This method returns true if
specified value match with current string object
o Example
Java
String endsWith
o
This method returns true if
the specified suffix is equal to the current string object suffix
o Example
Java
String equals
o
This method returns true.
If specified string equal to the current string object
o Example
Java
String format
o
This method returns the
format of the string as you want.
o This method contains two
arguments, one is format and second is format value
Example
Java
String getBytes
o
This method returns the
byte array of current string object
Example
Java
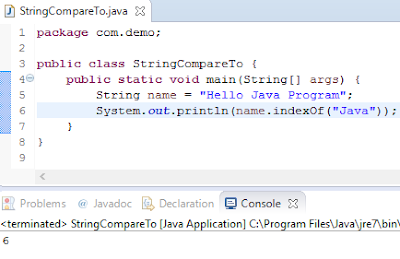
String indexOf
o
This method returns the
index of current string object or character etc.
Example
Java
String isEmpty
o
This method returns true if
the current string object is null or its length is 0.
Example
Java
String length
o This method returns the total length of current string object in
number format
Example
Java
String replace
o This method replaces the old element with new specified element
value.
Example
Java
String replaceAll
o This method replaces all the current string object with
specified regular expression. In below example I replace all white spaces with
tab.
Example
Java
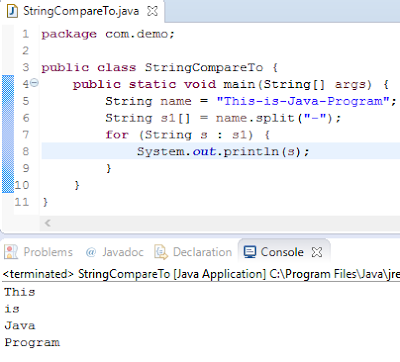
String Split
o This method returns the array by splitting the current string
object with given delimiter
Example
Java
String subString
o This method returns the sub part of current string object and
its index count start from 0.
Example
Java
String trim
o This method returns the string with leading and trailing white
spaces removed
Example
Java
String valueOf
o This method returns the string value by converting different types
of primitive data types
Example
String Object - creating String object Methods




















No comments:
Post a Comment